Advanced Stroke Life Support® Blended Learning
The ASLS Blended Learning Course educates healthcare professionals to identify, evaluate, and manage patients with stroke.
ASLS Blended is an innovative, 2-part web and skills curriculum developed by the Gordon Center with the American Heart Association, which made ASLS Blended a fourth discipline for its network of training centers
The ASLS Blended provider course covers 14 stroke scales and is available in three tracks:
- Prehospital
- In-Hospital
- Prehospital & In-Hospital (treating patients in both environments).
Modeled after the AHA’s HeartCode® offerings, ASLS Blended has two components:
Adaptive eLearning
- Individualized, tailored content
- Interactive graphics and animations
- Outcomes based – assessment drives content
- Portable, more easily updated
- Modular – user can stop and pick up again
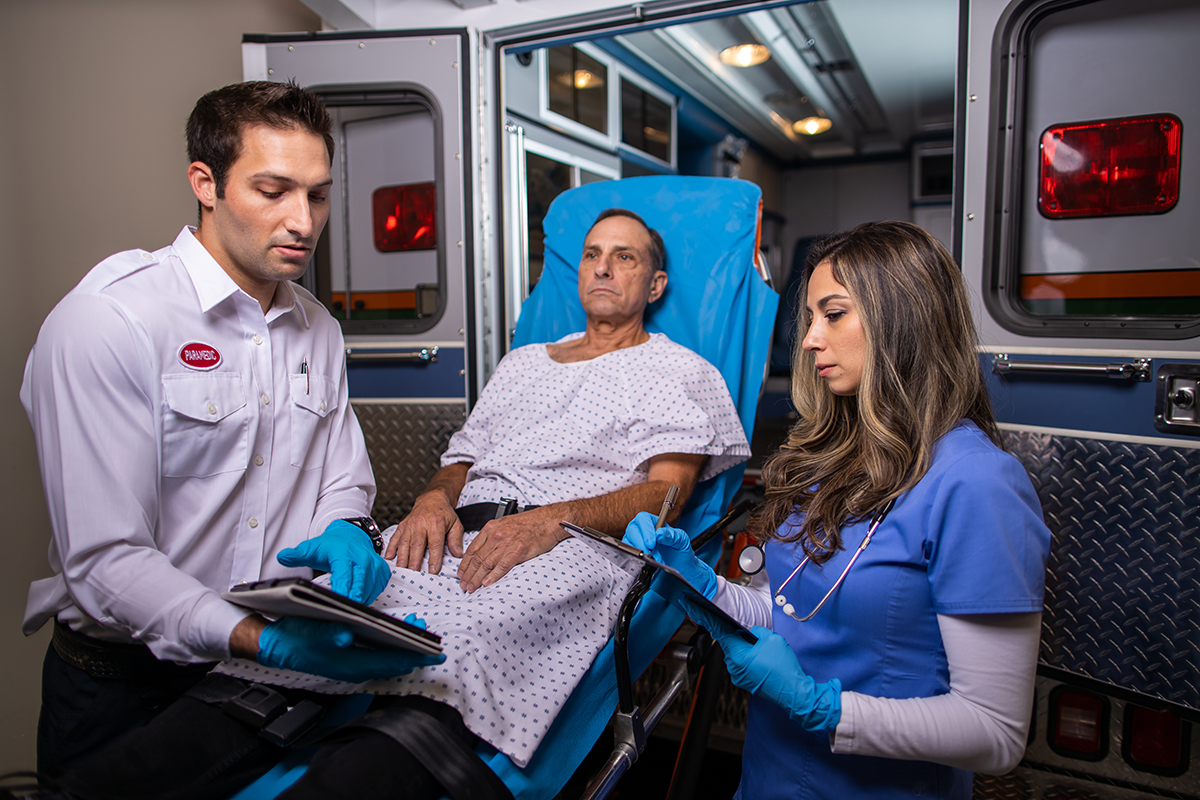
Skills demonstration – a 3-part, in-person session with an instructor, utilizing chosen stroke scale to:
- A - Examine a normal patient
- B - Identify a stroke syndrome or mimic and determine the best destination within their stroke system of care
- C - Undergo a stroke simulation scenario to manage common presentations or complications of stroke.
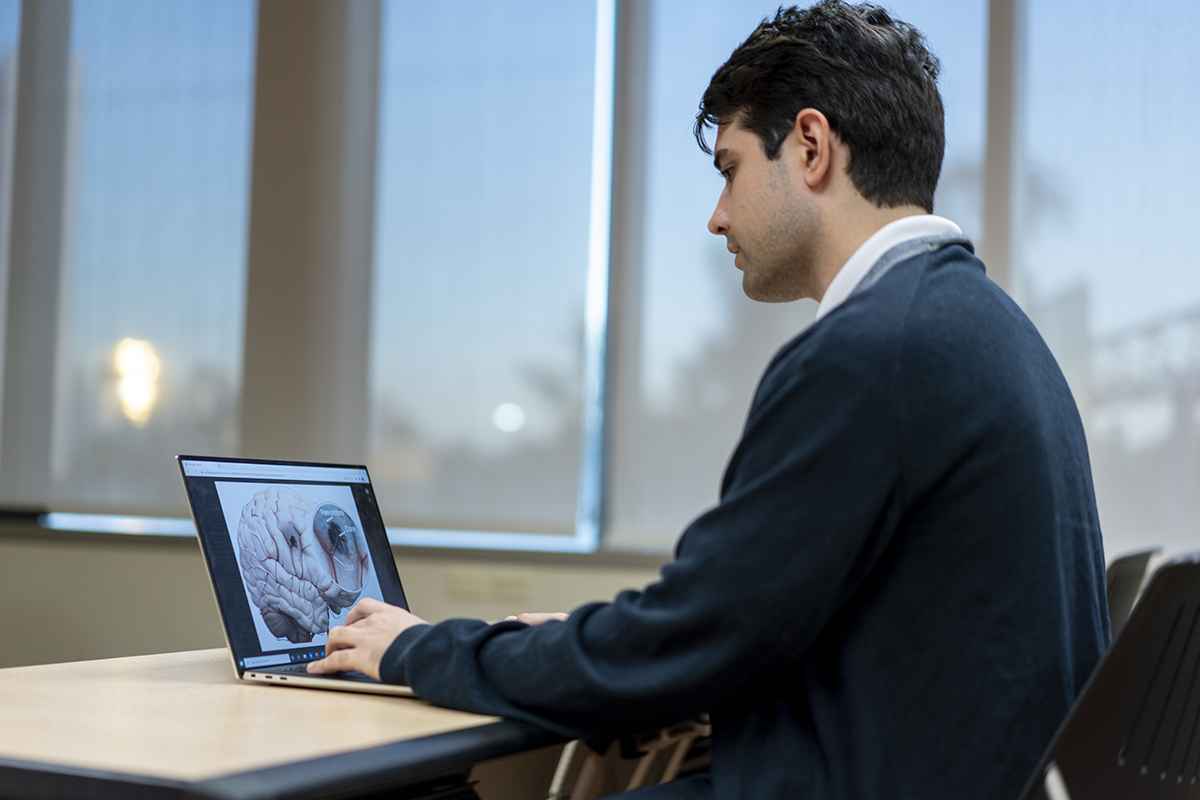
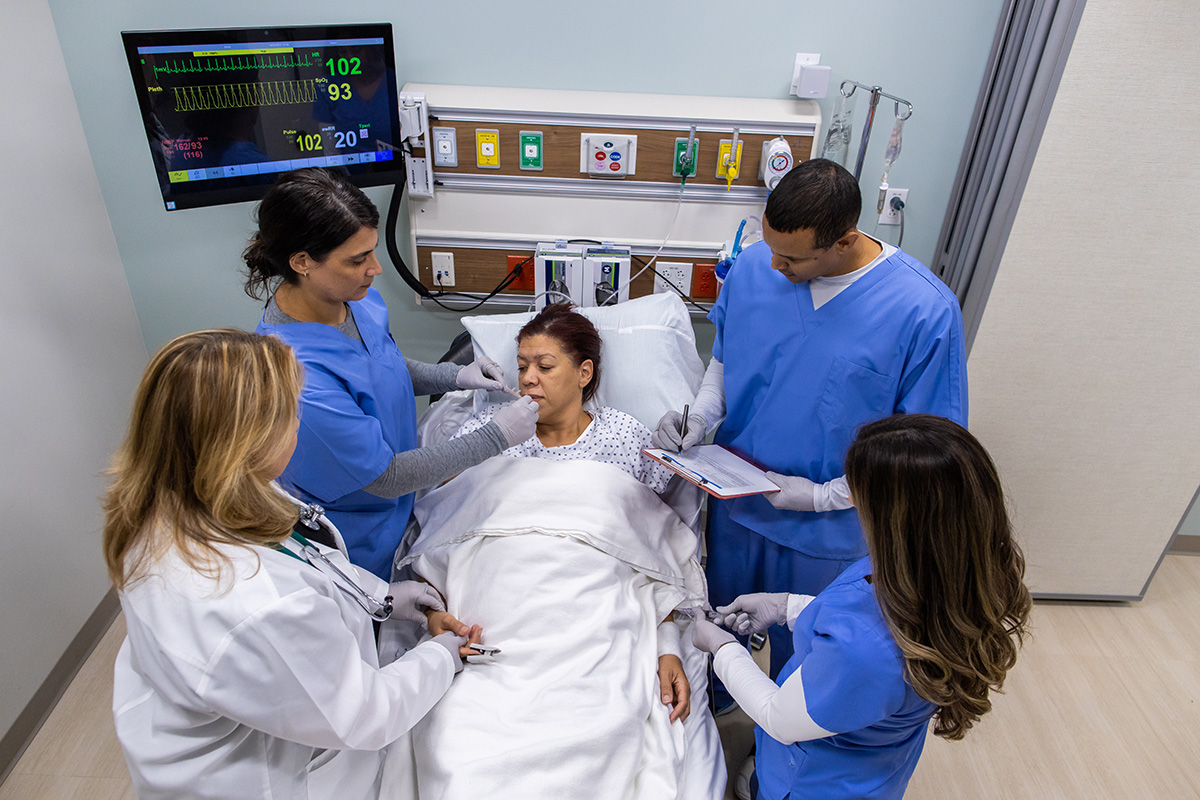

Originally created in 1998 by the Gordon Center
Developed by a team of expert paramedics, nurses, and physicians based on the latest research
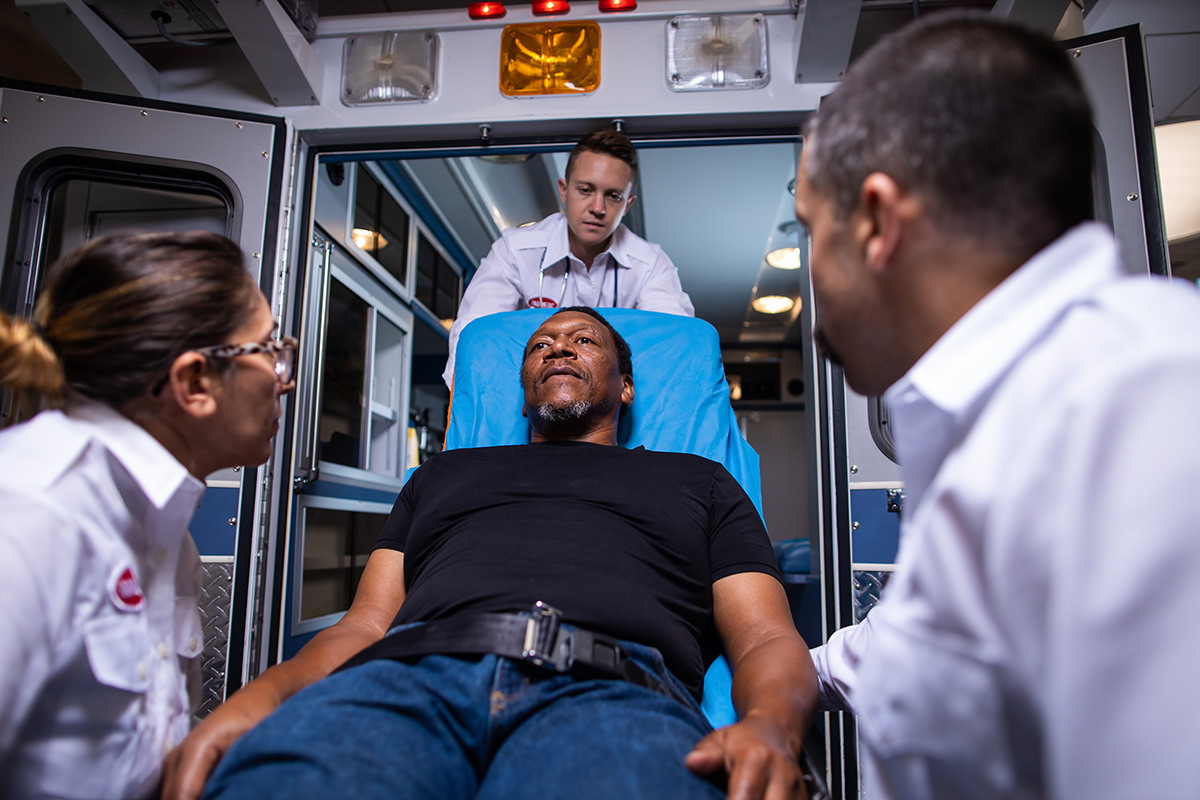
Advanced Stroke Life Support® was first developed as an instructor-led, hands-on training designed for prehospital providers on-scene, nurses, and physicians in the Emergency Department, and on through the continuum of care to the stroke or critical care unit. With this new collaboration with the AHA, the Gordon Center significantly expands its outreach throughout the United States. For learners, the online portion follows a continuously adapting path personalized by their input, not only their answers to content questions but also self-reported level of confidence. The in-person skills tests challenge learners to apply what they gained from the online portion to correctly perform neurologic exams, diagnose, and manage patients with stroke.
Becoming a Training Center
Are you an AHA ACLS Training Center or Instructor interested in learning more about the new Advanced Stroke Life Support (ASLS®) Blended Learning Course?
Read the
FAQs to learn more about becoming an AHA ASLS Training Center.
